How to Install and Configure LAMP stack on Arch Linux
LAMP => Linux — Apache —MySQL— PHP
Most of Web Applications runs on top of a stack consists of: an operating system (Linux) a web server, like Apache HTTP Server or nginx. a relational DBMS, like MySQL or PostgreSQL. a programming language, like PHP, Python or Perl
An example of such a stack is LAMP witch stand for four open source software: Linux, Apache, MySQL and PHP.
The article provides a step-by-step guide on how to install and configure the LAMP stack on Arch Linux.
Before You Begin
Before getting started with the installation process,check and update the Arch package database.
sudo pacman -Syu
Apache :
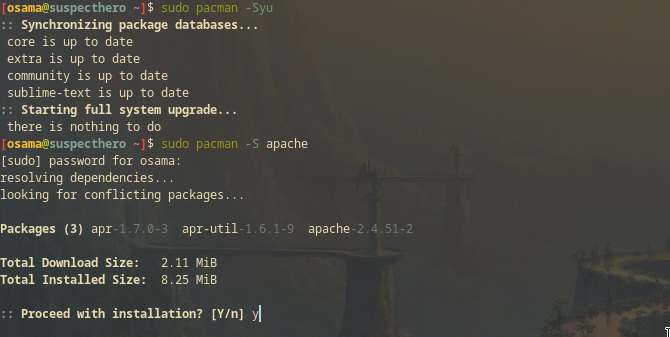
install Apache with the following command.
sudo pacman -S apache
open the main configuration file /etc/httpd/conf/**httpd.conf**. with your favorit editor and comment out the line
LoadModule unique_id_module modules/mod_unique_id.so
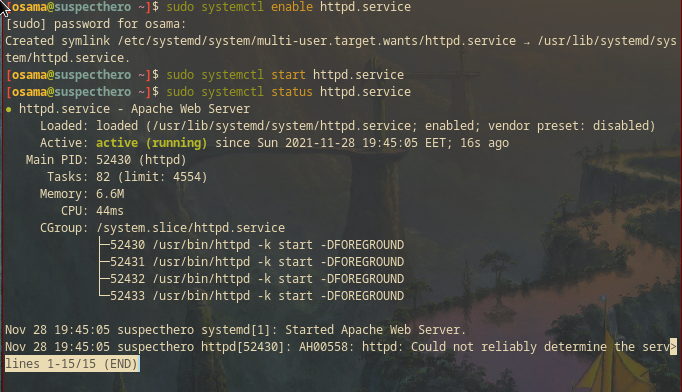
Set Apache to start at boot:
sudo systemctl enable httpd.service
start and check server process daemon.
sudo systemctl start httpd.service
sudo systemctl start httpd.service
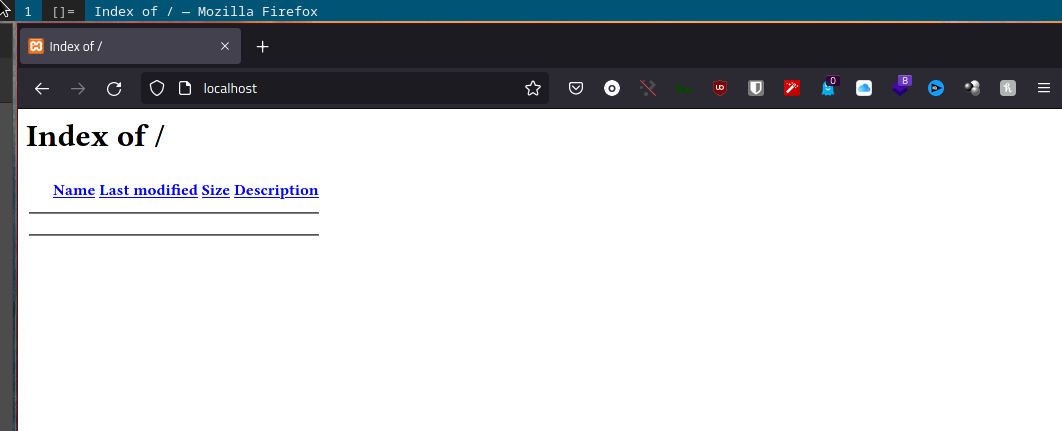
To check whether the apache server is running, open the browser and type localhost. The browser will display the following page:
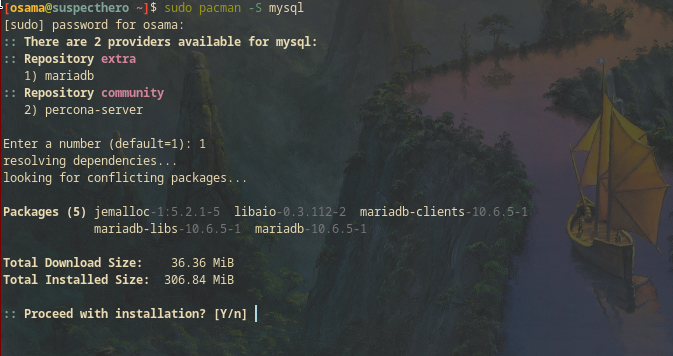
MySQL Database (MariaDB)
Install MySQL as follows:
sudo pacman -S mysql
choose mariadb repository.
Install the MariaDB data directory:
sudo mysql_install_db --user=mysql --basedir=/usr --datadir=/var/lib/mysql
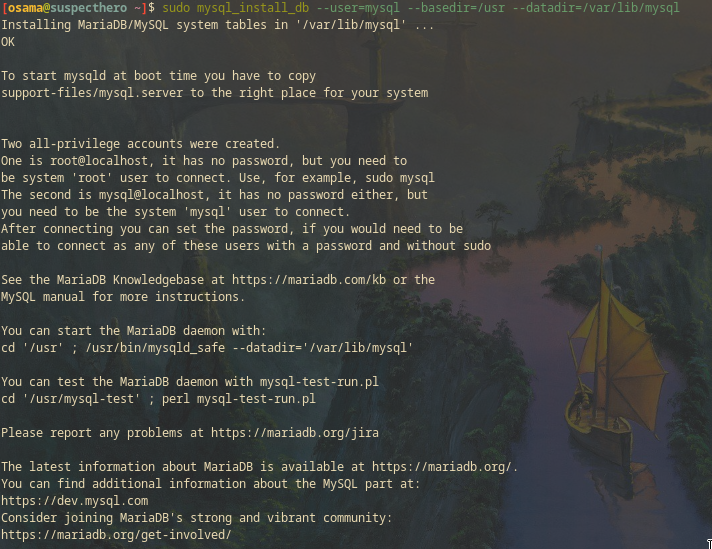
Start MariaDB and set it to run at boot:
sudo systemctl start mysqld.service
sudo systemctl enable mysqld.service
Run mysql_secure_installation, a program that helps secure MySQL and MariaDB. mysql_secure_installation gives you the option to set your root password, disable root logins from outside localhost, remove anonymous user accounts, remove the test database and then reload the privilege tables:
sudo mysql_secure_installation
follow the process of the installation and if you get stuck enter Y at evrey option.
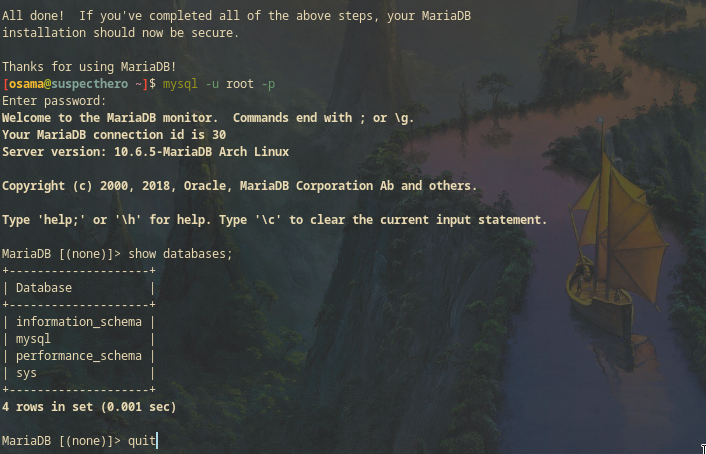
Verify MySQL database connectivity by running the following command then leave database shell with quit or exit statement.
mysql -u root -p
-u <user> specifies the user, and -p will prompt you for the password.
PHP
Install PHP:
sudo pacman -Syu php php-apache
Enable the PHP module in the /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf file by adding the following lines to the end of the file.
LoadModule php_module modules/libphp.so
AddHandler php-script php
Include conf/extra/php_module.conf

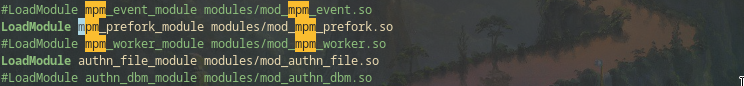
In the same file /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf, comment the line:
#LoadModule mpm_event_module modules/mod_mpm_event.so
and uncomment the line:
LoadModule mpm_prefork_module modules/mod_mpm_prefork.so
Restart the Apache:
sudo systemctl restart httpd.service
Test if PHP is working correctly, by creating a index.php file in /srv/http and add phpinfo():
sudo echo "<?php \n phpinfo(); \n ?>" >> /srv/http/index.php

hit back to the browser and type localhost to verify php setting.
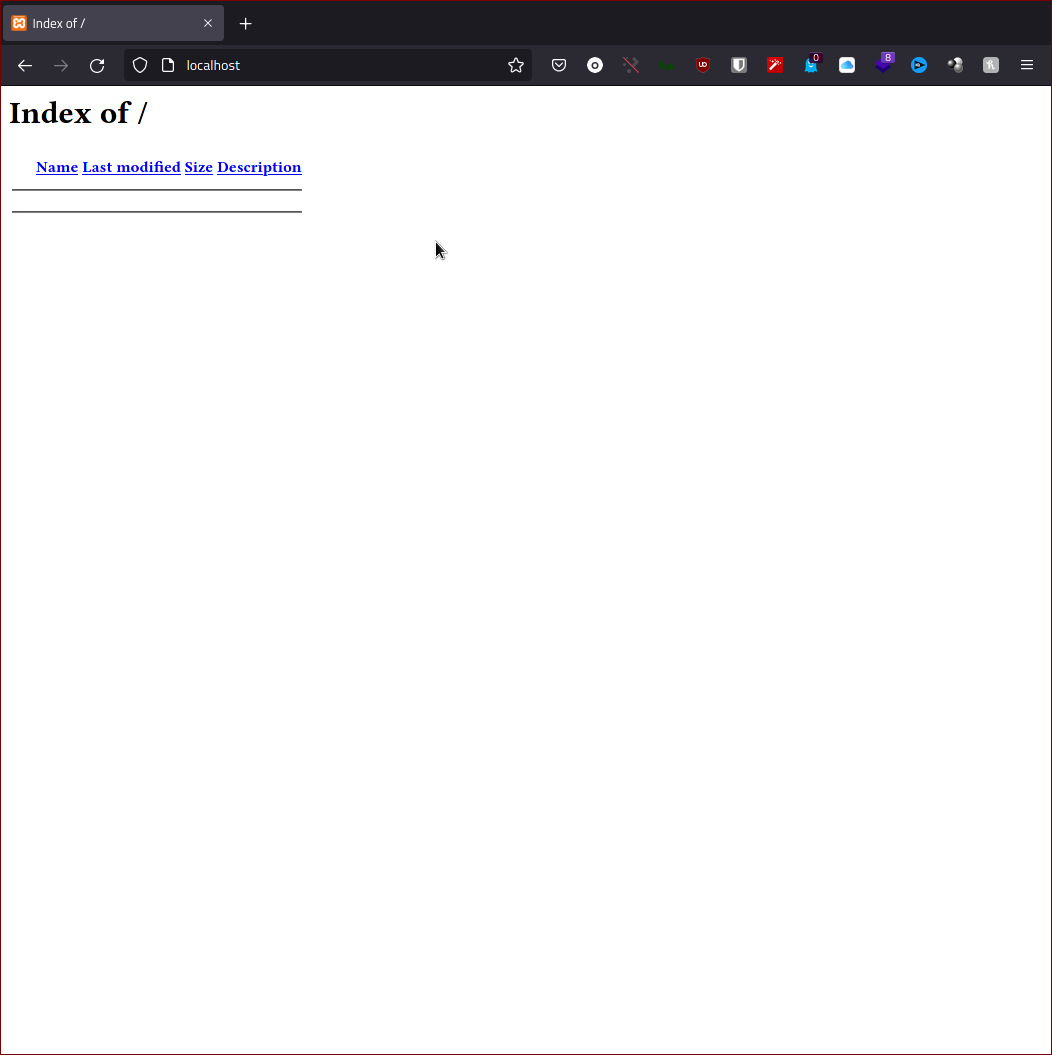
That’s it! If everything looks like image above, you now have PHP dynamic server-side scripting language enabled on Apache
If you want to verify Apache syntax configurations and see a list of loaded modules without restarting httpd daemon run the following commands.
sudo apachectl configtest
sudo apachectl -M
Install and Configuring PhpMyAdmin
If you don’t master MySQL command line and want a simple remote access to MySQL database provided through web interface then you need PhpMyAdmin package installed on your Arch.
sudo pacman -S phpmyadmin php-mcrypt
Open the file /etc/php/php.ini and uncomment the lines extension=mysqli, extension=pdo_mysql and extension=iconv by removing the semicolon (;)

Now set up Apache to work with phpmyadmin by creating phpmyadmin’s main configuration file.
sudo vim /etc/httpd/conf/extra/phpmyadmin.conf
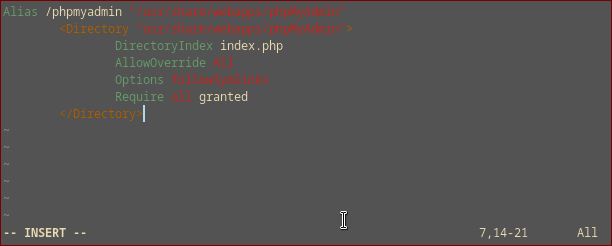
Next, include the path to this configuration file on Apache’s main configuration file. /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf

restart the Apache web service.
sudo systemctl restart httpd
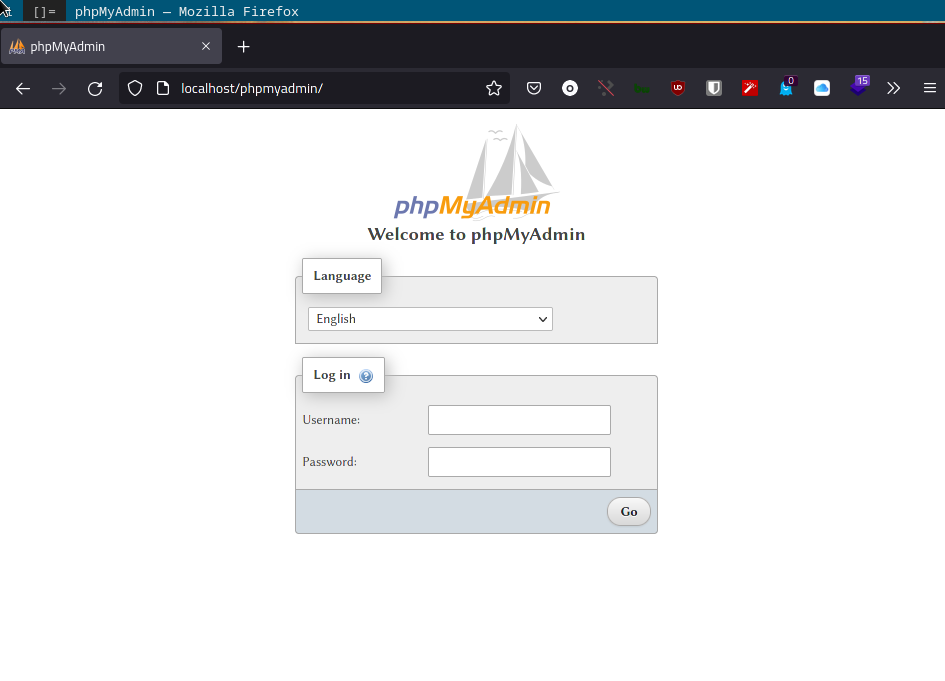
Now access the PhpMyAdmin from the browser.
http://localhost/phpmyadmin
With this article guide, you can comfortably start testing the behavior of your web app in a production-like environment.